Spatial Variation of Sediment Grain Size and Its Environmental Implications in the Anoi Itam Coastal Waters, Pulau Weh, Indonesia
Main Article Content
Abstract
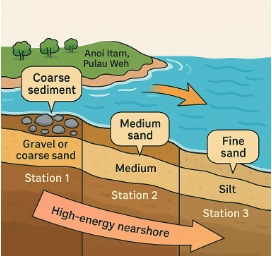
This study investigates the grain-size distribution and sediment characteristics of the Anoi Itam coastal waters, Sabang City, Aceh Province, Indonesia. The objective was to determine spatial variations in sediment texture and their relationship with hydrodynamic energy conditions and depositional environments. Sediment samples were collected from three stations representing distinct energy zones along the Anoi Itam coastal transect using a Van Veen grab sampler. Laboratory analysis employed the dry-sieving method, and grain-size fractions were classified following the Wentworth and Folk & Ward scales. The results revealed significant spatial variability among stations, reflecting a clear gradient of hydrodynamic energy. Station 1 was dominated by coarse and very coarse sands, indicating a high-energy nearshore environment. Station 2 exhibited a mixture of coarse and medium sands, representing moderate-energy transitional conditions, while Station 3 consisted mainly of medium to fine sands, typical of low-energy depositional zones. The overall trend shows progressive fining from Station 1 to Station 3, consistent with decreasing flow energy and increasing depositional stability. These findings demonstrate that sediment distribution in the Anoi Itam coastal system is primarily influenced by hydrodynamic sorting, geomorphological features, and sediment transport direction, providing essential baseline data for coastal management and environmental assessment.
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
References
1. Hoch, C.; Weaver, R.; Webb, B.; Resio, D.; Ward, N.; Lodge, C.; Kachouie, N. Predicting near-bed sediment transport through particle image velocimetry. Coast. Eng. Proc. 2023, 37, 9.
2. Huang, L.; Zhao, C.; Jiao, C.; Zheng, G.; Zhu, J. Quantitative analysis of rapid siltation and erosion causing coast-line evolution in the coastal mudflat areas of Jiangsu. Water 2023, 15(9), 1679.
3. Pagán, J.; Tenza-Abril, A.; Aragonés, L.; Villacampa, Y.; López, I. Classification of sediment quality according to its behavior in the accelerated particle wear test (APW). Sustainability 2021, 13(5), 2633.
4. Vieira, B.; Pinho, J.; Barros, J.; Carmo, J. Hydrodynamics and morphodynamics performance assessment of three coastal protection structures. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8(3), 175.
5. Sauvé, P.; Bernatchez, P.; Glaus, M. Identification of coastal defence measures best adapted to mitigate hazards in specific coastal systems: Development of a dynamic literature meta-analysis methodology. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10(3), 394.
6. Papasarafianou, S.; Siarkos, I.; Gkaifyllia, A.; Sahtouris, S.; Varra, G.; Chatzipavlis, A.; Tzoraki, O. A holistic ap-proach for coastal–watershed management on tourist islands: A case study from Petra–Molyvos Coast, Lesvos Island (Greece). Geosci. 2024, 14(12), 326.
7. Asiah, A.; Hisyam, E.; Hambali, R. Planning of coastal protection structures in the area of Arung Dalam Beach, Central Bangka. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1108(1), 012043.
8. Dimyati, M.; Trihatmoko, E.; Marfai, M. Ten years erosion–sedimentation monitoring: System-based automatic in-terpretation in coastal area of Brebes Regency, Central Java Province, Indonesia. Geogr. Tech. 2020, 16(1), 25–38.
9. Tenuta, M.; Dominici, R.; Donato, P.; Imbrogno, G.; Lirer, S.; Rosa, R. Approaches for the sustainable manage-ment of the Apulian coastal areas: The potential of a geoportal. Rend. Online Soc. Geol. Ital. 2023, 60, 37–50.
10. Lima, M.; Ferreira, A.; Coelho, C. A cost–benefit approach to assess the physical and economic feasibility of sand bypassing systems. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11(9), 1829.
11. Zhang, L.; Yan, J.; Zhao, B.; Xia, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, P. The rapidly evolving Fudu Estuary sandbar la-goon landform on the east coast of the Bohai Sea: Recent changes and mechanism. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9(12), 1350.
12. Rafati, Y.; Hsu, T.; Calantoni, J.; Puleo, J. Entrainment and transport of well-sorted and mixed sediment under wave motion. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2022, 127(8), e2022JC018686.
13. Schenone, S.; Hewitt, J.; Hillman, J.; Gladstone-Gallagher, R.; Gammal, J.; Pilditch, C.; Thrush, S. Seafloor sedi-ment microtopography as a surrogate for biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Ecol. Appl. 2024, 35(1), e3069.
14. Wang, H.; Titschack, J.; Wienberg, C.; Korpanty, C.; Hebbeln, D. The importance of ecological accommodation space and sediment supply for cold-water coral mound formation: A case study from the western Mediterranean Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 760909.
15. Bi, S.; Lai, H.; Guo, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Chen, X.; Li, G. The characteristics of intestinal bacterial community in three omnivorous fishes and their interaction with microbiota from habitats. Microorganisms 2021, 9(10), 2125.
16. Vandenberghe, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Lu, H. Diverse floodplain deposits of reworked loess in a mon-soon climate (Hanzhong Basin, Central China). Quat. Res. 2021, 103, 4–20.
17. Zayed, A.; El-Tapey, H.; Al-Toukhy, A. Sedimentation pattern of soils south El-Amiria, Alexandria Governorate, Egypt. Menoufia J. Soil Sci. 2021, 6(6), 183–196.
18. Kotlia, B.; Kukreti, M.; Bisht, H.; Palar, B.; Seiler, M.; Nadeauc, M.; Mehra, A. Palaeoenvironmental and palaeocli-matic conditions in the Bhimtal Valley, Kumaun Lesser Himalaya, between 40 and 24 ka using granulometric anal-ysis. J. Climate Change 2023, 9(4), 1–11.
19. Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Porz, L.; Arlinghaus, P.; Hanz, U.; Holtappels, M.; Schrum, C. Physical mechanisms of sedi-ment trapping and deposition on spatially confined mud depocenters in high-energy shelf seas. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2025, 130(7), in press.
20. Dietze, M.; Schulte, P.; Dietze, E. Application of end-member modelling to grain-size data: Constraints and limita-tions. Sedimentology 2021, 69(2), 845–863.
21. Feil, S.; von Eynatten, H.; Dunkl, I.; Schönig, J.; Lünsdorf, N. Inherited grain-size distributions: Effect on heavy-mineral assemblages in modern and ancient sediments. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2024, 129(2), e2023JF007356.
22. Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Sun, M.; Zeng, Y.; Chongyi, E. Investigating the Late Pleistocene to present-day deposition pro-cesses of paleofloods in the Yellow River–Huangshui River Valley through end-member modeling. Adv. Eng. Technol. Res. 2023, 4(1), 62.
23. Sun, X.; Filgueira, R.; Wang, N.; Han, M.; Guyondet, T.; Zhang, X. Vacuum effect: A redistribution process of or-ganic carbon mediated by bivalve farming. ACS ES&T Water 2023, 3(10), 3215–3222.